Premier Membership
Elixa Premier is for people interested in trying longevity pharmaceuticals, wellness technology and getting a snapshot of their current health.
+ Comprehensive Assessment
- Specialist Medical Consultation and Examination
- Latest Blood Panel Analysis and ECG
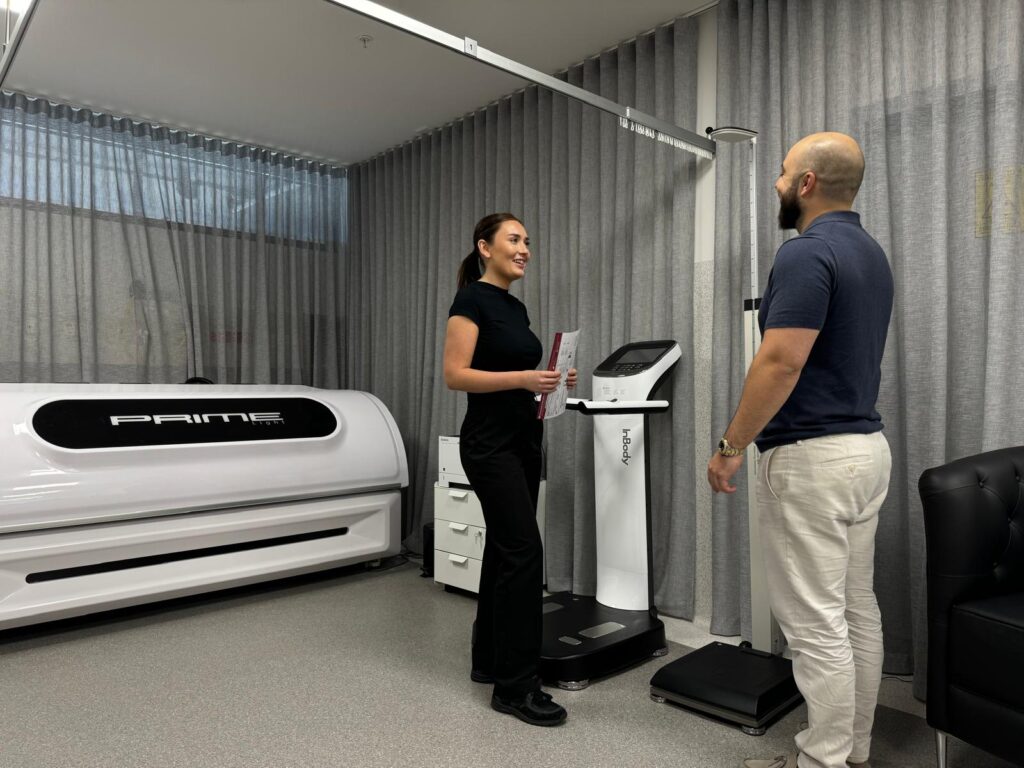
+ InBody Composition Scan Annually
+ Monthly Wellness Treatments
1 Session Of
- Cryotherapy
- Red Light Therapy
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Pod
- Infrared Sauna*
+ Elixa of Life Longevity Pharmaceuticals
- Elixa of Life Pharmaceuticals are high-quality pharmacy grade supplements specifically designed for Elixa Longevity and precision-compounded by our pharmacists.
- Enhance cellular function and longevity with Elixa Of Life’s proprietary pharmaceutical formulation. This advanced blend is designed to support mitochondrial health, promote efficient cellular repair, and help maintain optimal physiological function as you age—delivering the restorative benefits essential to healthy ageing.
- Our formula brings together powerful age-defying ingredients to support vitality, wellbeing, and a longer, healthier life—one capsule at a time
Note: This Membership is a minimum 6 Month Commitment with payments debited monthly in advance.
*Only available at selected locations
Gold Membership
Elixa Gold is for people who are committed increasing their lifespan and improving their health. Gain valuable insights, uncover potential risks and work towards improving key longevity markers.
+ Comprehensive Assessment
- Specialist Medical Consultation and Examination
- Latest Blood Panel Analysis and ECG
+ InBody Composition Scan Monthly
+ Monthly Wellness Treatments
2 Sessions Of
- Cryotherapy
- Red Light Therapy
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Pod
- Infrared Sauna*
+ Elixa of Life Longevity Pharmaceuticals
- Elixa of Life Pharmaceuticals are high-quality pharmacy grade supplements specifically designed for Elixa Longevity and precision-compounded by our pharmacists.
- Enhance cellular function and longevity with Elixa Of Life’s proprietary pharmaceutical formulation. This advanced blend is designed to support mitochondrial health, promote efficient cellular repair, and help maintain optimal physiological function as you age—delivering the restorative benefits essential to healthy ageing.
- Our formula brings together powerful age-defying ingredients to support vitality, wellbeing, and a longer, healthier life—one capsule at a time
+ Elixa of Life – Monthly IV Infusions
-
Recharge your body and mind with our monthly IV Vitality infusion. Specially formulated to support cellular repair, boost energy levels, and promote mental clarity, this treatment is ideal for those looking to enhance overall wellbeing and fight everyday fatigue.
Note: This Membership is a minimum 12 Month Commitment with payments debited monthly in advance.
*Only available at selected locations
Platinum Membership
Elixa Platinum is for people serious about living longer, feeling youthful and looking great. Get a clear picture and understanding of your current health, identify potential risks and receive a personalised longevity plan.
+ Comprehensive Assessment
- Specialist Medical Consultation and Examination
- Nutritional Consultation and assessment with specialist dietitian and personalised plan with emphasis on longevity
- Latest Blood Panel Analysis and ECG Advanced
- Biological Age Test (GrimAge) with advanced DNA Methylation test
+ InBody Composition Scan Monthly
+ Monthly Wellness Treatments
4 Sessions Of
- Cryotherapy
- Red Light Therapy
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Pod
- Infrared Sauna*
+ Elixa of Life Longevity Pharmaceuticals
- Elixa of Life Pharmaceuticals are high-quality pharmacy grade supplements specifically designed for Elixa Longevity and precision-compounded by our pharmacists.
- Enhance cellular function and longevity with Elixa Of Life’s proprietary pharmaceutical formulation. This advanced blend is designed to support mitochondrial health, promote efficient cellular repair, and help maintain optimal physiological function as you age—delivering the restorative benefits essential to healthy ageing.
- Our formula brings together powerful age-defying ingredients to support vitality, wellbeing, and a longer, healthier life—one capsule at a time
+ Elixa of Life – Monthly IV Infusions
+ IV Vitality Infusion
- Recharge your body and mind with our monthly IV Vitality infusion. Specially formulated to support cellular repair, boost energy levels, and promote mental clarity, this treatment is ideal for those looking to enhance overall wellbeing and fight everyday fatigue.
+ IV Longevity Infusion
- Designed to support healthy ageing and metabolic balance, our monthly IV Longevity infusion promotes internal wellness and cellular resilience. This treatment helps strengthen your body’s natural defences and encourages long-term vitality.
Note: This Membership is a minimum 12 Month Commitment with payments debited monthly in advance.
*Only available at selected locations
Additional Add-On IV Infusions Available
Elixa Platinum is for people who desire to live longer, look younger and feel great.
+ Elixa of Life – IV Vitality Infusion
- Recharge your body and mind with our monthly IV Vitality infusion. Specially formulated to support cellular repair, boost energy levels, and promote mental clarity, this treatment is ideal for those looking to enhance overall wellbeing and fight everyday fatigue.
+ Elixa of Life – IV Wellness Infusions: IV Detox Plus Infusion
- Support your body’s natural detoxification processes and restore vitality with our IV Detox Plus infusion.
- This treatment is designed to assist with energy production, promote cellular cleansing, and help you feel lighter and more refreshed from the inside out.
+ Elixa of Life – IV Wellness Infusions: IV Immunity Plus Infusion
- Boost your body’s natural defences with our IV Immunity Plus infusion.
- This formula is designed to support immune resilience, energy levels, and recovery, making it the perfect monthly companion for those wanting to stay well and energised year-round.